Monthly Archives: July 2025
IEC 62052-11, Electricity metering equipment (AC)- General requirements, tests and test conditions -Part 1l:Metering equipment IEC 62053 -21, Electricity metering equipment (AC) – Static meters for active energy (classes 1 and 2) IEC 62053 -23, Electricity metering equipment (AC)- Static meters for reactive energy(classes 2 and 3) IEC 62055-31., Electricity metering – Payment systems, particular […]
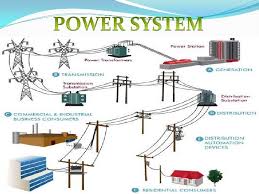
An electric power system is a network of electrical components deployed to supply, transfer, and use electric power. An example of a power system is the electrical grid that provides power to homes and industries within an extended area. The electrical grid can be broadly divided into the generators that supply the power, the transmission […]
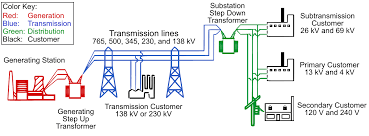
An electrical grid (or electricity network) is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids consist of power stations, electrical substations to step voltage up or down, electric power transmission to carry power over long distances, and finally electric power distribution to customers. In that last step, voltage is stepped down […]
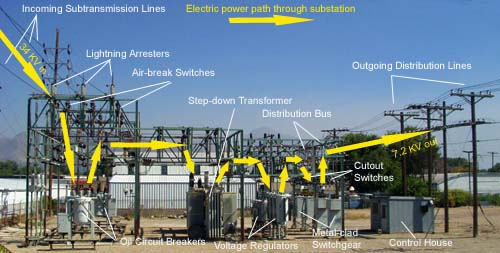
A substation is a part of an electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, or perform any of several other important functions. Between the generating station and consumer, electric power may flow through several substations at different voltage levels. A substation may include transformers to change […]
A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electrical grid. Many power stations contain one or more generators, rotating machine that converts mechanical power into three-phase electric power. The […]
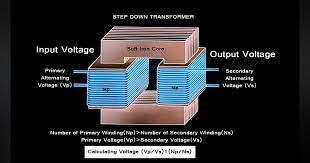
In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer’s core, which induces a varying electromotive force (EMF) across any other coils wound around the […]
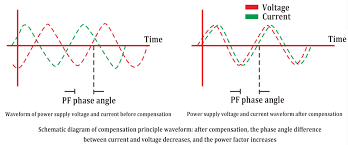
When reactive power devices, whether capacitive or inductive, are purposefully added to apower network in order to produce a specific outcome, this is referred to as compensation.
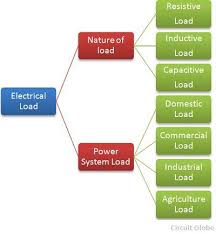
An electrical load is an electrical component or portion of a circuit that consumes (active) electric power,[1][2] such as electrical appliances and lights inside the home. The term may also refer to the power consumed by a circuit. This is opposed to a power supply source, such as a battery or generator, which provides power.[2] The term is used more broadly in electronics for a device connected to a signal source, whether or not it consumes power.[2] If an electric circuit […]
- 1
- 2